What is a Digital Business Model?
A brief explanation and introduction

Definition of digital disruption
A digital business model is a form of creating value based on the development of customer benefits using digital technologies. The aim of the digital solution is to generate a significant advantage for which customers are willing to pay.
The development of digital business models is an important task for companies being confronted with digitalization and digital disruption. The mere extension of an existing analogue business model by a digital component (e.g. online ordering of goods from a stationary retailer) is a preliminary stage, but not an independent digital business model.
Characteristics of digital business models
Digital business models have different characteristics, several of which usually apply simultaneously.
The added value generated would not be possible without the use of digital technologies. Amazon, Uber and Airbnb are companies that would have no business without the technologies of the Internet. Amazon might be a local marketplace today, Airbnb a room agency in several cities and Uber a taxi center or a carpool agency.
The business model is characterized by digital business innovation. Digital business models are based on services that are new to the market.
Customer acquisition and distribution are based on digital channels. Companies that develop and drive digital business models mostly use digital technologies to reach potential audiences. Sales are characterized by trends such as sales automation and early onboarding. (see Freemium Model)
Customers are willing to pay for the digital service or the service. Digital business models thus create a unique customer value that can be monetized.
The willingness of customers to pay and thus the independent creation of value is a striking feature of a digital business model. Purely digital services, e.g. the possibility of monitoring energy consumption via an app, are digital offers, but not digital business models.
Types of digital business models
Freemium model
Customers receive parts of the digital service (e.g. limited functions of software) free of charge. This serves to manage the onboarding process with as little sales effort as possible.
The Freemium model follows the principle of competence standardization: Previously personnel-intensive activities such as sales were made more efficient by automatic processes. The challenge for companies is to successfully manage the upgrade from the Freemium version to a paid version.
Marketplace model
Similar to Amazon, a digital platform functions as an intermediary marketplace for products and services: Supply and demand are brought together. Digital business models that follow this model derive their added value from the fact that a large number of independent players are active on the marketplace and regular transactions take place.
The marketplace model can work alone or represent the extension of an existing offer of a company. A property management company that allows external service providers such as cleaning staff or the bakery service to be integrated into a tenant app already has a digital business model in the form of a marketplace – although in this case only on a very small scale.
Using instead of buying
This digital business model enables another form of use of an asset (e.g. software, automobile or machine). It is no longer the possession, but the consumption or use of an asset that is monetarized. Digital technologies make it possible to measure consumption or usage. In the field of car sharing, for example, both the rental and the return as well as the kilometres or miles driven are billed. In the case of machines, payments can be made, for example, according to the operating time, the number of units produced or other data retrieved from the machine.
Digital business models based on the “use instead of buy” principle can help companies to reach new target groups (e.g. those who have been reluctant to invest so far) or to remain competitive and to offer customers an attractive digital business model before potential competitors do so.
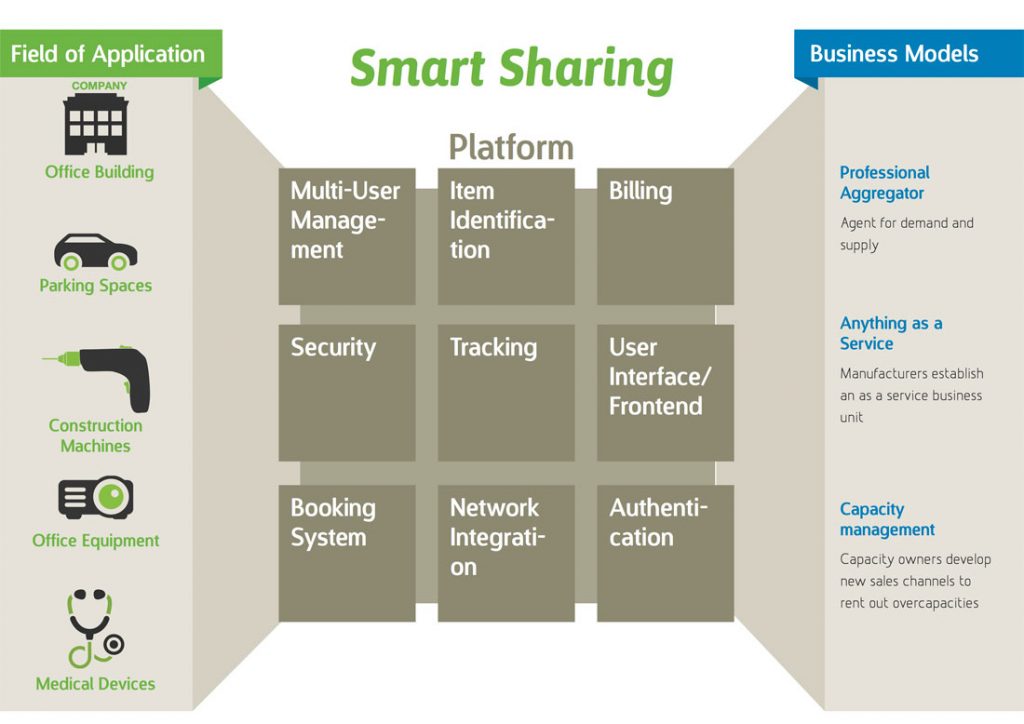
Example of a digital business model in the sharing economy.
Development of a digital business model

Toothbrushes can become digital business models.
There are a number of questions to answer when developing a digital business model. These questions are discussed as part of an innovation process in innovation management, often using methods such as Open Innovation. The focus is on future customer benefits.
This will be explained using the example of a toothbrush and a drilling machine. The customer’s benefit is not the possession of the toothbrush, but clean and healthy teeth. Also, owning a drilling machine is not the customer benefit, it is the hole. If it would be possible to sell holes in the wall digitally, this digital business model would certainly be a strong competitor for drill manufacturers.
The development of digital business models therefore begins with a profound analysis of a company’s future role in the market:
- What is the real problem behind buying existing products?
- Where do your existing products and services solve these problems well?
- Where do problems exist that have not yet been solved?
- In which areas does a product possibly create new problems that have not yet been solved?
- What problems and challenges do customers face in developing their own digital business models?
- What problems and challenges will customers face in the future?
Digital business models for a mechanical engineering company
Digital business models: New markets for mechanical engineering companies
This is illustrated by the example of a mechanical engineering company. So far, the machines have helped companies to manufacture products highly efficiently. However, extensive problems in connection with the use of the machine were not solved:
- Fluctuations in orders: The company has to cope with volatility in orders. Sometimes the machines are not working at full capacity, at other times production capacity would have to be increased. By connecting machines and developing a marketplace, the machine builder can offer valuable additional services: utilization-oriented invoicing ( use instead of purchase ) or a brokerage of production capacities (“marketplace model”) can be the basis for successful digital business models.
- Staff training: Monitoring the machine requires precise training, which is costly and time-consuming. Teams of experts must be on site in each shift to monitor the machine. Error messages must be detected and corrected on site. This requires precise shift planning to ensure that qualified staff are available around the clock. The machine manufacturer can develop digital business models as a solution here: for example an online academy for improved training or a 24-hour service center with networked technicians who monitor the performance of machines worldwide and, if necessary, switch on via web conferences.
- Lack of skilled workers: In future, customers of the machine manufacturer will have more and more difficulties finding qualified personnel to operate and maintain the machines. For the mechanical engineering company, this gives them the opportunity to establish their own worldwide online academy and offer qualifications as a digital business model.The development of digital business models is therefore initially based on an intensive analysis of current and future customer problems. The second step is a technology analysis: a list of the technological possibilities to solve the identified customer needs with the help of digital technologies.
Characteristics of digital business models
A digital business model is the result of the interaction between customer needs and possible available technologies. Companies that develop digital business models often use innovation management methodologies here. Prototypes are developed, which are tested and verified in the market. When developing a digital business model, it is not crucial to develop the “perfect” digital business model from the very first second. The innovation process is iterative and characterized by many loops. The Innolytics Innovation Software supports idea generation and the development of a Digital Roadmap for digital business models.