What is disruptive innovation?
A brief explanation and introduction

Disruptive innovation – radical change of markets and business models
Disruptive innovation refers to the establishment of new, previously unknown business innovation like products or services, which can begin as a small niche innovation and trigger a market revolution. Disruptive innovation has a strong potential for growth. It supersedes existing processes, displaces market leaders and redefines industry rules. Disruptive innovation is also referred to as breakthrough innovation or radical innovation. In the context of digitalization, the term digital disruption is used.
Disruptive innovation – radical change of markets and business models
The difference between incremental and disruptive innovation
The difference between incremental and disruptive innovation will be explained using the example of an automobile manufacturer:
The introduction of e-mobility and the emergence of disruptive digital technologies are confronting companies with new challenges. Although e-mobility has been discussed in politics and the economy for years, digital technologies are increasingly bringing about rapid change, leading to disruptive changes in markets and business models. This is disruptive innovation.
Model maintenance and the development of new models largely falls within the area of innovation on the basis of existing technologies and can therefore be assigned more to the defined area of incremental innovation.
Disruptive innovation is difficult to master with conventional innovation management and idea management: The same innovation process that is useful and conducive to a model change in the automotive industry can inhibit the development of disruptive innovation. Companies need to strengthen their innovation capability to manage change and overcome organizational and mental barriers among employees.
The challenge of managing disruptive innovation
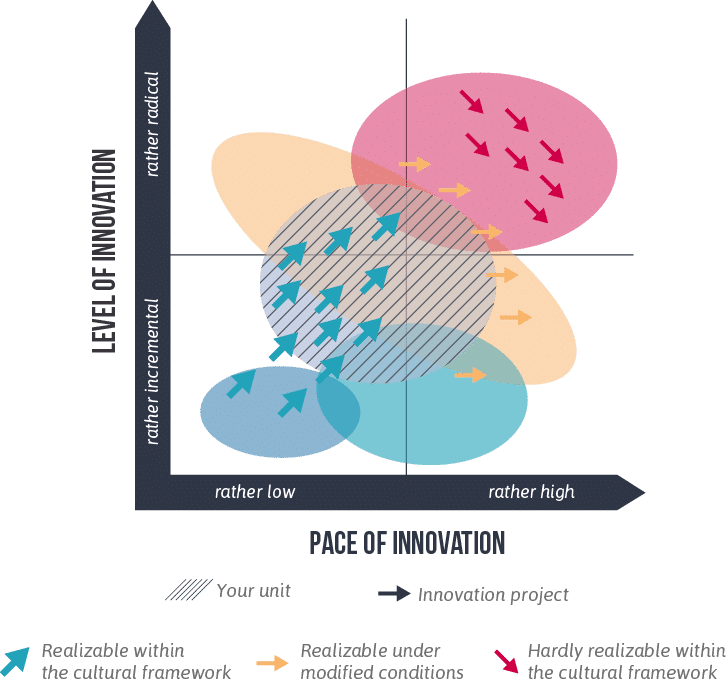
In innovation management, companies today have to manage a greater variety of innovations. The chart illustrates the challenge facing companies: They have to manage different degrees of innovation at the same time. This requires different types of innovation cultures, various innovation processes and diverse roles within projects.
However, companies are often culturally oriented only towards the implementation of one type of innovation, such as incremental innovation. The illustration shows that companies are often unable to cope with the discrepancy between the different types of innovation.
Incremental Innovation
Disruptive Innovation
Procecure
Linear and continuous path, from concept to commercialization, predetermined steps.
Numerous discontinuities and gaps. The disruptive innovation process is often inconsistent.
It is characterized by many stops and process changes due to unexpected events, results and discoveries.
Generation of ideas and search for opportunities
Idea generation and the identification of opportunities happen at the beginning: Critical events are recognized long before they occur.
Idea generation and the search for opportunities happen inconsistently, often as a reaction to irregularities in the course of the project.
Process
A formal, approved process that ranges from idea generation and development to commercialization.
While developing disruptive innovation, the formal process only has real value if the project enters into later stages of development.
Business Case
A complete and detailed plan can be drawn up due to the relatively low uncertainty at the beginning of the process.
The business model develops through the discovery-oriented technology and market insights, the business plan arises when the uncertainty decreases.
Players
Employees assigned to an interdisciplinary team with clear tasks and responsibilities in the specialist area.
Key figures come and go in the early project phases, many are part of an informal network around the project, they usually are multidisciplinary.
Organizational structures
Usually, an interdisciplinary team works within the business unit.
The project often starts in research and development, is transferred into some form of incubator organization, later into a goal-oriented organization.
Resources and competencies
The project team has all the skills needed for the process. The project is subject to the standard resource distribution process.
Creativity and skills in the acquisition of resources and competencies – from inside and outside – are crucial for the survival and success of the project.
Involvement of the operational units
Operational units are involved from the beginning.
Informal involvement of operational units is important, but the project must not be absorbed by them too early.
Disruptive innovation by small companies
Very often start-ups develop new products or services and create new markets with a high willingness to take risks based on new technologies or innovative business models. It is not large corporations that write the success stories about disruptive innovation, but often small, young companies. They are flexible and do not have rigid hierarchies that tend to prevent innovation. Since large companies react cautiously to new technologies and market developments, they face the risk of being driven out of the market by companies that are striving for success.
Disruptive innovation turns industries upside down
The drivers of disruptive innovation have the courage to turn the rules of their industry upside down and redefine them. They create unknown new markets, which in turn enable previously unknown business models, and thus open up new customer groups.
Disruptive innovation – what is its concept for success?
Companies that are successful with disruptive innovations are looking for so-called hidden needs. To this end, they rely on methods such as open innovation and co-creation, i.e. they directly involve potential customers. They recognize trends and market gaps that promise a high potential. They are willing to take risks when entering the market – financially, technologically and entrepreneurially.
Digitalization as a driver for disruptive innovation
In the past, inventions such as the steam engine and electric light were the driving forces behind breakthrough changes and technological developments. In our time, the Internet is the opportunity for small businesses to develop exciting, revolutionary services and digital products and become successful with them. There are interesting, useful apps for smartphones, and technologies such as m2m and LTE provide the basis for technological developments and innovative digital products. Our world, as we know it today, will be completely connected in a few years and previously unimaginable markets will have arisen through disruptive innovation.