Innovation Process
The Starter’s Guide

New approaches to a successful innovation process
The innovation process is a key element of contemporary innovation management. Innovations can be implemented transparently and effectively. In this article, you will learn everything you need to know to define and implement an innovation process in your organization.
- What is an Innovation Process? (Definition)
- Example of an Idea Management and Innovation Process
- Linear and Agile Innovation Processes
- The Most Important Factors for a Highly Successful Innovation Process
- Criticism of the classic innovation process
- Drive innovation processes through to implementation
What is an Innovation Process? (Definition)
Especially in complex projects such as the development of innovative technologies, processes are of great importance. For example, in the 1960s, NASA developed pioneering innovation processes such as Phased Project Planning to enable the management of development projects.
- The NASA innovation process served primarily for control: the clear division of the process into different phases was intended to prevent errors from being transferred from one state to the next.
- Methods such as the Stage-Gate process which has been developed by Robert G. Cooper adopted the NASA method and developed it further.
The general idea is to divide the innovation process into stages and gates: The development takes place in different stages, whereby the gates are decision points.
An innovation process is an organizational method that divides the uncertainties within an innovation project into clearly subdivided steps and decision points to drive development forward efficiently, while at the same time avoiding potential risks.
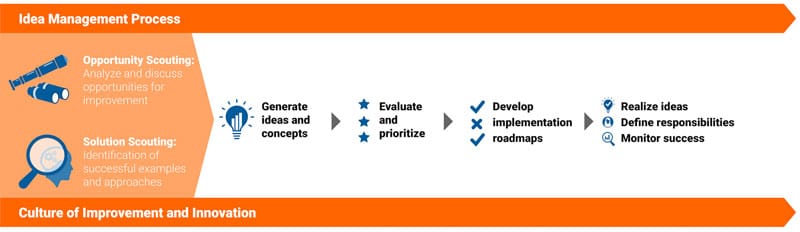
Example of an Idea Management and Innovation Process
In this chart, you can see the typical workflow of an innovation process. Although innovation processes within companies are different, they often follow a similar logic.
In the beginning, the search for opportunities and solutions that others have developed elsewhere stands in the foreground. This stage is the so-called phase of the “fuzzy front-end of innovation”.
The phase of idea generation follows this. Employees develop ideas, concepts, and innovative solutions. Here, companies often rely on innovation challenges and utilize the so-called “swarm intelligence” of a crowd.
Ideas are evaluated and prioritized – often by an innovation committee or by employees and managers in an innovation network.
The best ideas are further developed into innovative concepts. Innovation projects are launched and listed in the form of an innovation roadmap.
In the implementation phase, innovation teams realize innovation successfully.
Constant measurement of innovation ensures that key performance indicators are achieved.
Linear and Agile Innovation Processes
The innovation process often fails due to the implementation of ideas in practice. What is the reason for this? What barriers prevent an innovation process from operating efficiently? And how can companies develop innovation processes that fit their strategic challenges?
In recent years, so-called “linear innovation processes” like the Stage-Gate Process have increasingly come under criticism because they focus merely on incremental innovation.
- Traditional concepts of innovation processes assume a linear process from the search for opportunities to their implementation, which is not always the case in practice.
- The same management methods that lead to incremental innovation projects to success might cause innovation projects with a higher degree of innovation to fail.
- Correspondingly, companies tend towards incremental innovation.
Especially for the development of higher degrees of innovation – radical innovations or disruptive innovations – the concept of a linear innovation process doesn’t work. Agile processes and concepts like innovation labs are needed.
Innovation labs and agile innovation processes
Companies need to drive different types of innovation: Product development, service innovation, business model innovation, or digital business models. This variety cannot be structured in a standardized innovation process.
Outside the daily business, employees work on an innovation project – sometimes together with customers or suppliers. The project is driven forward from initial ideation to realization.
- In an innovation lab, small and agile teams with intrinsically motivated employees act like independent startups.
- Tight deadlines and internal pitchings can significantly speed up the innovation process.
- Employees develop innovations with more passion, creativity, and energy.
Within innovation labs, agile innovation processes are used to enable employees to react quickly to discoveries and developments.
The Most Important Factors for a Highly Successful Innovation Process
The requirements for developing an innovation process vary from one company to another. For instance, this depends on the different innovation strategies. Nevertheless, there are several success factors and building blocks that have proven to be particularly useful.
Identify market opportunities: Following an analysis of trends, customer needs, and business competencies, the innovation process will initially show how future offerings must be designed to create new markets.
Develop ideas: In the innovation process, new ideas for products, services, and business models are generated by applying creativity techniques and inspirations.
Putting together teams: Within the company, multidisciplinary start-up teams have formed that work autonomously with entrepreneurial thinking and acting.
Marketing ideas: In pitchings, management concepts have to be put to the test time and again. This encourages the development and maturation of the best ideas.
Rapid prototyping: Prototypes increase the speed of development and minimize the risk of errors. Consumer-oriented market tests and iterative development loops contribute to a fast optimization of the innovation process.
Innovation culture: Team members are trained as innovation advisers. They learn to apply the innovation methods and pass on their know-how. The innovation process supports the establishment of an enterprise-wide innovation culture. Within innovation labs, agile innovation processes are used to enable employees to react quickly to discoveries and developments.
Criticism of the classic innovation process
In recent years, so-called “linear innovation processes” have increasingly come under criticism. Innolytics® Managing Director Dr. Jens-Uwe Meyer: “One reason could be that classic processes adopt a linear process from the search for opportunities to their implementation, which is not always the case in practice. The same management methods that lead incremental innovation projects to success might possibly cause innovation projects with a higher degree of innovation to fail. Correspondingly, companies seem to have a tendency towards incremental innovation.”
In the free Innolytics® study “Think Further in Innovation Management” you will learn more about how companies can align their innovation process with different types of innovation (incremental innovations, radical innovations, digital innovations, etc.).
Especially for the development of higher degrees of innovation – radical or disruptive innovations – the classical innovation process is only of limited suitability. In his book “Radical Innovation“, Dr. Jens-Uwe Meyer presents the model of the Innovation Greenhouses, in which teams develop new ideas outside the traditional innovation process.

Drive innovation processes through to implementation
A trendy, high-turnover product is to be developed. Up to now, everything has been thought of and duly considered in the innovation process: problems and needs have been analysed and the company’s possibilities defined. Numerous ideas have been developed. For weeks now, several concepts have been lying in the drawer that only need to be put into practice. But that’s where they stay. For years, until another company suddenly has the same idea – and realises it.
Download your free study “Think Further in Innovation Management” (worth 178€) right now.